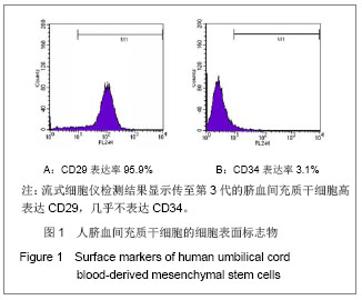
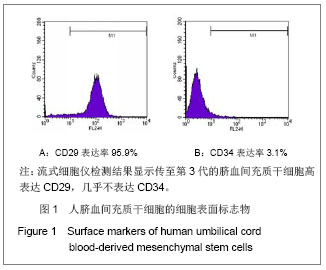
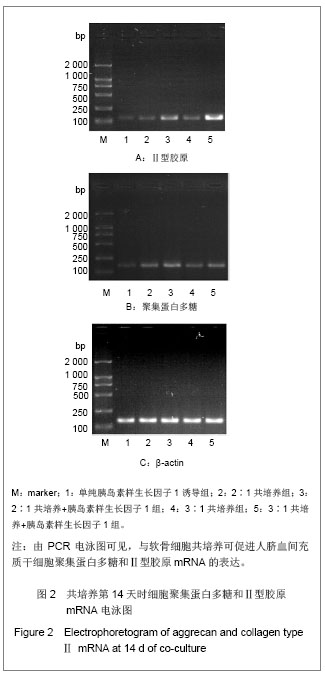
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (23): 4196-4203.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.23.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chondrogenic differentiation of co-cultured human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Zheng Peng-fei, Chen Lei, Dong Zhan, Jiang Li, Ju Li, Wang Ru-fa, Lou Yue
- Nanjing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2013-06-04Published:2013-06-04 -
Contact:Lou Yue, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Nanjing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China yuelounjmu@sina.com -
About author:Zheng Peng-fei★, Master, Attending physician, Nanjing Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China fei19840101@126.com -
Supported by:grants by Nanjing Municipal Health Bureau, No. QYK10163*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Peng-fei, Chen Lei, Dong Zhan, Jiang Li, Ju Li, Wang Ru-fa, Lou Yue. Chondrogenic differentiation of co-cultured human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(23): 4196-4203.
share this article
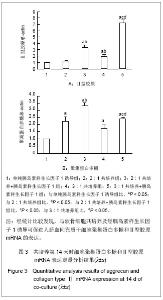
诱导第14天时,不同比例人脐血间充质干细胞与软骨细胞共培养的细胞聚集蛋白多糖mRNA的表达明显高于单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导组(P < 0.05),而Ⅱ型胶原mRNA的表达除2∶1共培养组与单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导组比较差异无显著性意义外(P > 0.05),2∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组、3∶1共培养组和3∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组的表达均明显高于单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导组(P < 0.05)。说明共培养效果较单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导整体效果更好。在人脐血间充质干细胞与软骨细胞比例相同时,加用胰岛素样生长因子1后聚集蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达增加(P < 0.05)。同样培养条件不同细胞比例组间比较显示,3∶1共培养组较2∶1共培养组Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达高(P < 0.05),而聚集蛋白多糖mRNA的表达则2∶1共培养组高于3∶1共培养组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);同样与2∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组比较,3∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组Ⅱ型胶原mRNA表达明显增高(P < 0.05),而聚集蛋白多糖mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05),见图3。"
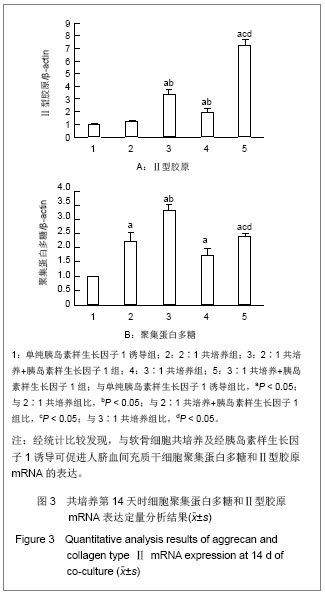

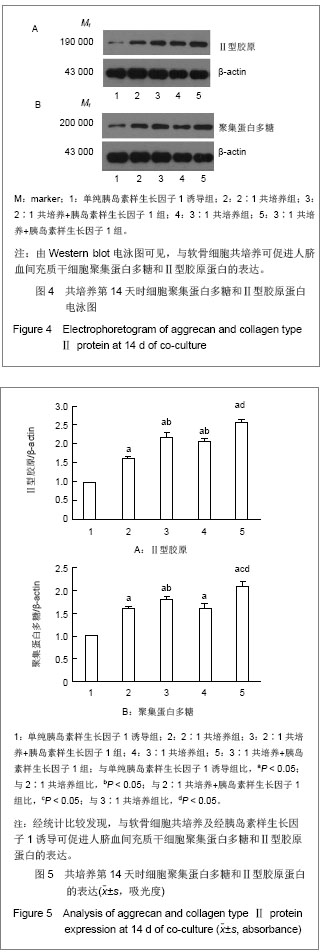
2.4 不同方法诱导后人脐血间充质干细胞聚集蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的表达 见图4,5。 培养第14天时,不同比例人脐血间充质干细胞与软骨细胞共培养的细胞聚集蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的表达明显高于单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导组(P < 0.05),说明共培养效果较单纯胰岛素样生长因子1诱导整体效果更好。相同比例人脐血间充质干细胞与软骨细胞共培养时,加用胰岛素样生长因子1后可使聚集蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达增加。同样培养条件不同细胞比例组间比较显示,3∶1共培养组较2∶1共培养组Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达高(P < 0.05),而聚集蛋白多糖蛋白的表达则2∶1共培养组高于3:1共培养组,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);与2∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组比较,3∶1共培养+胰岛素样生长因子1组聚集蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达均有所增高。"
| [1]Yu Y, Ren H, Yun W, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondroblast and osteoblasts. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008;25(6):1385-1389. [2]Kim SS, Kwon DW, Im I, et al. Differentiation and characteristics of undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells originating from adult premolar periodontal ligaments. Korean J Orthod. 2012;42(6):307-317.[3]La Rocca G, Lo Iacono M, Corsello T, et al. Human Wharton's Jelly mesenchymal stem cells maintain the expression of key immunomodulatory molecules when subjected to osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation in vitro: new perspectives for cellular therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. In press.[4]France LA, Scotchford CA, Grant DM, et al. Transient serum exposure regimes to support dual differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. In press.[5]Solorio LD, Dhami CD, Dang PN, et al. Spatiotemporal regulation of chondrogenic differentiation with controlled delivery of transforming growth factor-β1 from gelatin microspheres in mesenchymal stem cell aggregates. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(8):632-639.[6]Ronzière MC, Perrier E, Mallein-Gerin F, et al. Chondrogenic potential of bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Mater Eng. 2010; 20(3):145-158.[7]Chen WH, Lai MT, Wu AT, et al. In vitro stage-specific chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells committed to chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):450-459. [8]Hwang NS, Varghese S, Puleo C, et al. Morphogenetic signals from chondrocytes promote chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007;212(2):281-284.[9]Wu L, Leijten JC, Georgi N, et al. Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells increase chondrocyte proliferation and matrix formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(9-10): 1425-1436. [10]Karlsson C, Brantsing C, Svensson T, et al. Differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes: analysis of chondrogenic potential and expression pattern of differentiation-related transcription factors. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(2):152-163.[11]Mo XT, Guo SC, Xie HQ, et al. Variations in the ratios of co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes regulate the expression of cartilaginous and osseous phenotype in alginate constructs. Bone. 2009;45(1): 42-51. [12]Lettry V, Hosoya K, Takagi S, et al. Coculture of equine mesenchymal stem cells and mature equine articular chondrocytes results in improved chondrogenic differentiation of the stem cells. Jpn J Vet Res. 2010;58(1):5-15.[13]Fischer J, Dickhut A, Rickert M, et al. Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62(9):2696-2706. [14]Erickson IE, van Veen SC, Sengupta S, et al. Cartilage matrix formation by bovine mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture is age-dependent. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(10):2744-2753.[15]Meretoja VV, Dahlin RL, Kasper FK, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis in co-cultures with articular chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27): 6362- 6369. [16]Wei A, Chung SA, Tao H, et al. Differentiation of rodent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into intervertebral disc-like cells following coculture with rat disc tissue. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(9):2581-2595. [17]Xu L, Wang Q, Xu F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells downregulate articular chondrocyte differentiation in non-contact coculture systems: implications in cartilage tissue regeneration. Stem Cells Dev. In press.[18]Tsuchiya K, Chen G, Ushida T, et al. The effect of coculture of chondrocytes with messenchymal stem cells on their cartilaginous phenotype in vitro. Mater Sci Eng. 2004;24(3): 391-396.[19]Broxmeyer HE. Biology of cord blood cells and future prospects for enhanced clinical benefit. Cytotherapy. 2005; 7(3):209-218.[20]Zhang X, Hirai M, Cantero S, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood: reevaluation of critical factors for successful isolation and high ability to proliferate and differentiate to chondrocytes as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(4):1206-1218.[21]Feng X, Tian S, Sun K, et al. Effect of platelet lysate on chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(10):1250-1255.[22]Yang SE, Ha CW, Jung M, et al. Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells developed in cultures from UC blood. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(5):476-486.[23]Koch TG, Heerkens T, Thomsen PD, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from equine umbilical cord blood. BMC Biotechnol. 2007;7:26.[24]Lu X, Alshemali S, de Wynter EA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from CD34(-) human umbilical cord blood. Transfus Med. 2010;20(3):178-184. [25]Yu J, Cao H, Yang J, et al. In vivo hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood after transplantation into mice with liver injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;422(4):539-545.[26]Qian H, Wang J, Wang S, et al. In utero transplantation of human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells partially repairs injured liver in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2006;18(4):633-642. [27]The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance suggestion of caring laboratory animals. 2006-09-30.[28]Wajsfisz A, Makridis KG, Djian P. Arthroscopic retrograde osteochondral autograft transplantation for cartilage lesions of the tibial plateau: a prospective study. Am J Sports Med. In press.[29]Cameron JA, Milner DJ, Lee JS, et al. Employing the biology of successful fracture repair to heal critical size bone defects. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. In press.[30]Lee KB, Wang VT, Chan YH, et al. A novel, minimally-invasive technique of cartilage repair in the human knee using arthroscopic microfracture and injections of mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic Acid-a prospective comparative study on safety and short-term efficacy. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2012;41(11):511-517.[31]Giannoni P, Lazzarini E, Ceseracciu L, et al. Design and characterization of a tissue-engineered bilayer scaffold for osteochondral tissue repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. In press.[32]Chen X, Zhang F, He X, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in type I collagen-hydrogel for cartilage engineering. Injury. In press.[33]Ravichandran R, Seitz V, Reddy Venugopal J, et al. Mimicking Native Extracellular Matrix with Phytic Acid-Crosslinked Protein Nanofibers for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Macromol Biosci. In press.[34]Kosuge D, Khan WS, Haddad B, et al. Biomaterials and scaffolds in bone and musculoskeletal engineering. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. In press.[35]Lin G, Garcia M, Ning H, et al. Defining stem and progenitor cells within adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17: 1053-1063.[36]Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, et al. Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell. 2007;131(2):324-336.[37]Baksh D, Song L, Tuan RS. Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(3):301-316.[38]Toai TC, Thao HD, Thao NP, et al. In vitro culture and differentiation of osteoblasts from human umbilical cord blood. Cell Tissue Bank. 2010;11(3):269-280. [39]Fan X, Liu T, Liu Y, et al. Optimization of primary culture condition for mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood with factorial design. Biotechnol Prog. 2009;25(2): 499-507. [40]Kosmacheva SM, Volk MV, Yeustratenka TA, et al. In vitro growth of human umbilical blood mesenchymal stem cells and their differentiation into chondrocytes and osteoblasts. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2008;145(1):141-145.[41]Acharya C, Adesida A, Zajac P, et al. Enhanced chondrocyte proliferation and mesenchymal stromal cells chondrogenesis in coculture pellets mediate improved cartilage formation. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(1):88-97.[42]Wu L, Prins HJ, Helder MN, et al. Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in chondrocyte co-cultures are independent of culture conditions and cell sources. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(15-16):1542-1551.[43]Zhu S, Zhang T, Sun C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium alginate gel modified by hTGF-β1 for the construction of tissue-engineered cartilage in three-dimensional conditions. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(1): 95-101.[44]Qing C, Wei-ding C, Wei-min F. Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular matrix components. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2011;44(4):303-310.[45]Shintani N, Siebenrock KA, Hunziker EB. TGF-ß1 Enhances the BMP-2-Induced Chondrogenesis of Bovine Synovial Explants and Arrests Downstream Differentiation at an Early Stage of Hypertrophy. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53086.[46]Ertan AB, Y?lgor P, Bayyurt B. Effect of double growth factor release on cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. In press.[47]Li JW, Guo XL, He CL, et al. In vitro chondrogenesis of the goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells directed by chondrocytes in monolayer and 3-dimetional indirect co-culture system. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(19): 3080-3086. [48]Liu X, Zhou GD, Lü XJ, et al. Potential of chondrogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells co-cultured with chondrocytes on biodegradable scaffold: in vivo experiment with pigs and mice. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007;87(27):1929-1933. [49]Luo W, Fan J, Ye C. Proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of precartilaginous stem cells in self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffolds. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;26(12):1505-1511.[50]Aung A, Gupta G, Majid G, et al. Osteoarthritic chondrocyte-secreted morphogens induce chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(1):148-158. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [3] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [4] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [6] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [7] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [8] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [13] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [14] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [15] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||